The American Cancer Society states that colorectal cancer starts in the colon. “Most colorectal cancers start as a growth on the inner lining of the colon or rectum. These growths are called polyps.”
While polyps are quite common and often noncancerous, some can turn into cancer over time.
Historically, this form of cancer was typical for the older population, but as more and more young people are diagnosed with it, researchers are rethinking screening recommendations and are looking for different treatment approaches.
Statistics say that colorectal cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in US, with 153,020 being diagnosed with the disease in 2023 and over 52,000 dying of it.
Rebecca Siegel from the American Cancer Society believes that the increase of early-onset colorectal cancer at young people can be related to the lifestyle changes introduced in the mid-20th century.
Also, a study highlights one particular condition that shows no to little symptoms; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
This term refers to a range of conditions caused by a build-up of fat in the liver.
NAFLD doesn’t pose danger as such, but if the condition advances, it can lead to more serious issues such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and kidney disease.
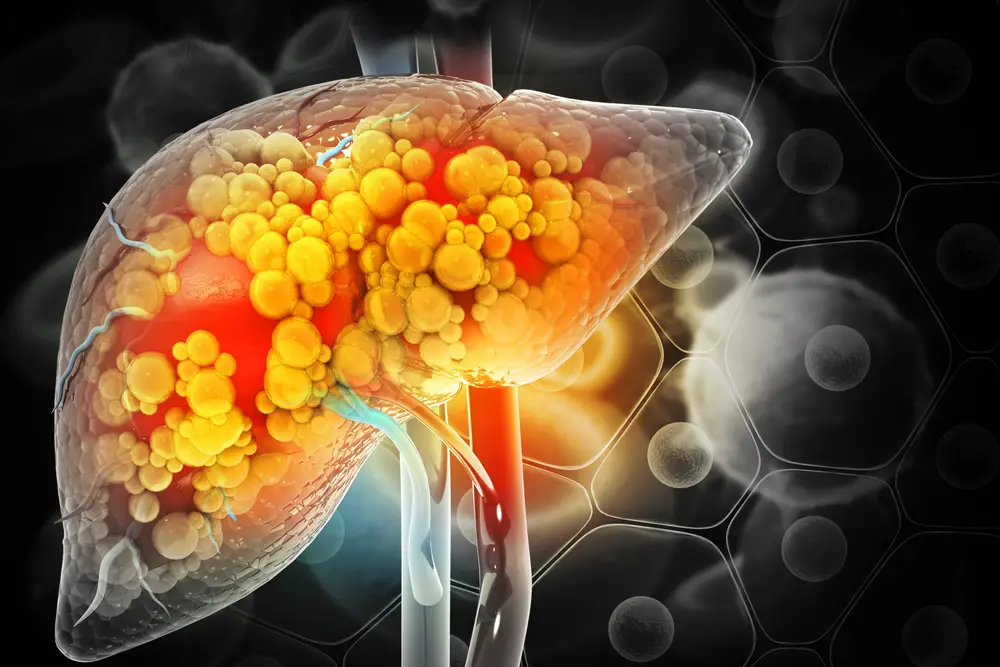
According to a study conducted by a team of researchers from South Korea, people aged under 50 with history of NAFLD are 24% more likely to be diagnosed with colon cancer compared to those who don’t suffer from the condition.
Although more research needs to be done, researchers do make a connection between colon cancer and the “silent” condition of NAFLD.

“Our findings revealed a strong link between NAFLD and early-onset CRC in young adults, suggesting the importance of implementing effective preventive strategies, particularly in populations with a growing burden of metabolic dysfunction,” experts said on the study published in ScienceDirect.
“These findings highlight the need for multifaceted preventive strategies, including lifestyle interventions and expanded screening for younger populations with NAFLD.”
According to the study, the inflammation caused by NAFLD may travel to the colon, triggering cancerous cells to develop.
Please SHARE this article with your family and friends on Facebook.
Bored Daddy
Love and Peace

