Known as “the mineral of the moment,” his majesty magnesium delivers health benefits most of us can’t even imagine.
Magnesium is a mineral crucial for normal bone structure in the body. Most people get magnesium from a balanced diet and foods rich in it. In fact, when thinking of foods that are a good source of this mineral, just think of fiber.
According to WebMD, “dietary sources of magnesium include legumes, whole grains, vegetables (especially broccoli, squash, and green leafy vegetables), seeds, and nuts (especially almonds). Other sources include dairy products, meats, chocolate, and coffee.”
This essential mineral is involved in more than 300 enzymatic processes in the body and helps maintain a healthy and functioning immune system, muscles, and nerves.
Among the rest, magnesium helps manage diabetes, help with pain in the bones, lessens anxiety, and helps with constipation.
1. Osteoporosis and Bone Pain
This mineral helps control the levels of calcium in the body and keep the bones healthy. Lack of it causes reduced bone mass and increases the risks of fractures.
How to take it for this condition:
- Take glycinate or magnesium citrate for improved absorption.
- A recommended daily dosage for an adult is 300–400 mg combined with Vitamin D and calcium.
- Consume seeds (sunflower, pumpkin), nuts (almonds, cashews), and leafy greens (spinach, Swiss chard).
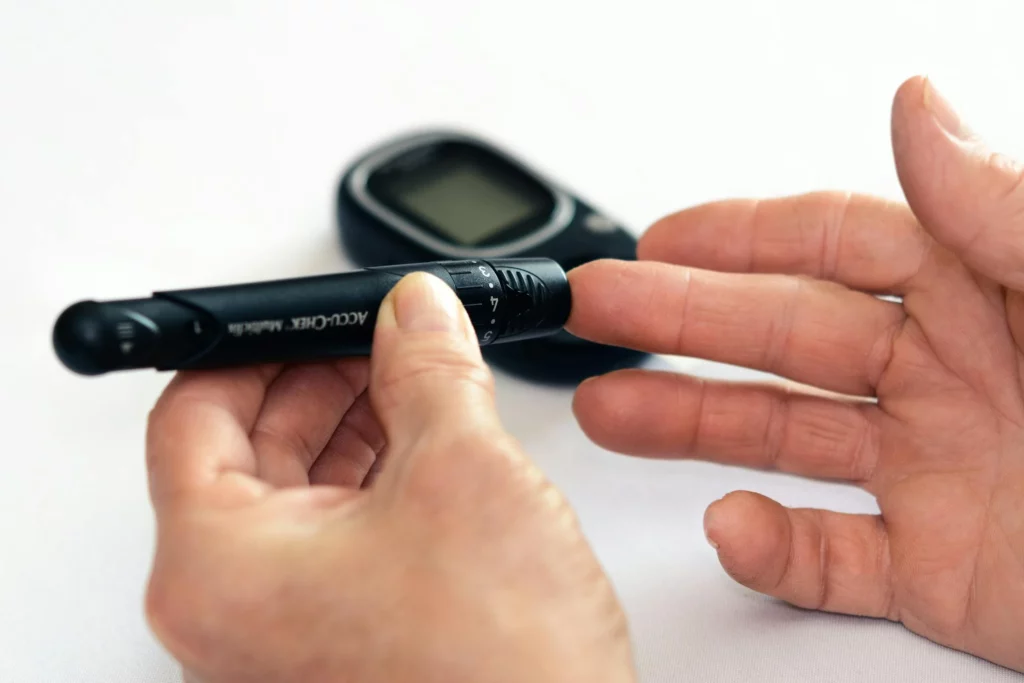
2. Blood Sugar Management and Diabetes
A number of studies have linked low magnesium levels with an increased risk of Type 2 diabetes.
How to take it for this condition:
- Magnesium taurate or chloride are the recommended forms (taurine also helps regulate insulin).
- The suggested daily intake is 250–350 mg, ideally taken after meals to help reduce spikes in blood sugar levels.
- Have dark chocolate, beans (black beans, lentils), and whole grains (quinoa, brown rice).
3. Depression and Anxiety
Among the rest, this precious mineral helps regulate neurotransmitters like serotonin and GABA, which play key roles in mood and mental well-being. Deficiency of it increases stress and leads to clinical depression, some researches suggest.
How to take it for this condition:
- Opt for magnesium threonate.
- The daily dosage to help fight depression and anxiety is 200–400 mg.
4. Digestive problems and constipation
Magnesium helps with constipation by bringing water into the intestines to make stools softer and easier to pass. It also relaxes the muscles in your digestive system to support smoother bowel movements.
How to take it for this condition:
- For digestive issues, consider magnesium citrate or oxide.
- Take 400–500 mg at night.
- Don’t use magnesium laxatives for more than a few days straight unless your doctor says it’s okay.
- Drink plenty of water.
Symptoms of magnesium deficiency include:
- a loss of appetite
- nausea or vomiting
- fatigue or weakness
- muscle cramps
- numbness
- seizures
- heart rhythm changes or spasms
People who experience kidney issues should avoid taking magnesium.
*Disclaimer: This information is for informational purposes only and not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult your physician or healthcare provider with any questions about your health or medications. Do not disregard professional advice based on this information.
Please SHARE this article with your family and friends on Facebook.
Bored Daddy
Love and Peace