Lucas Jemeljanova, a 13-year-old boy from Belgium, captured the global attention achieving something that was previously considered impossible.
This brave young man became the first ever person in the world to beat a deadly brain cancer known as diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG).
Hopeless and helpless after receiving the devastating diagnosis about Lucas’ cancer at the age of six, his family waited for him to respond to the treatments, and after everything failed, they enrolled him in the BIOMEDE trial in France, a venture exploring novel treatments for DIPG.
To the surprise and delight of many, young Lucas responded remarkably to the drug everolimu. MRI scans showed the tumor vanishing little by little.
He stopped using the medications a year and a half ago, and his tumor remained absent.
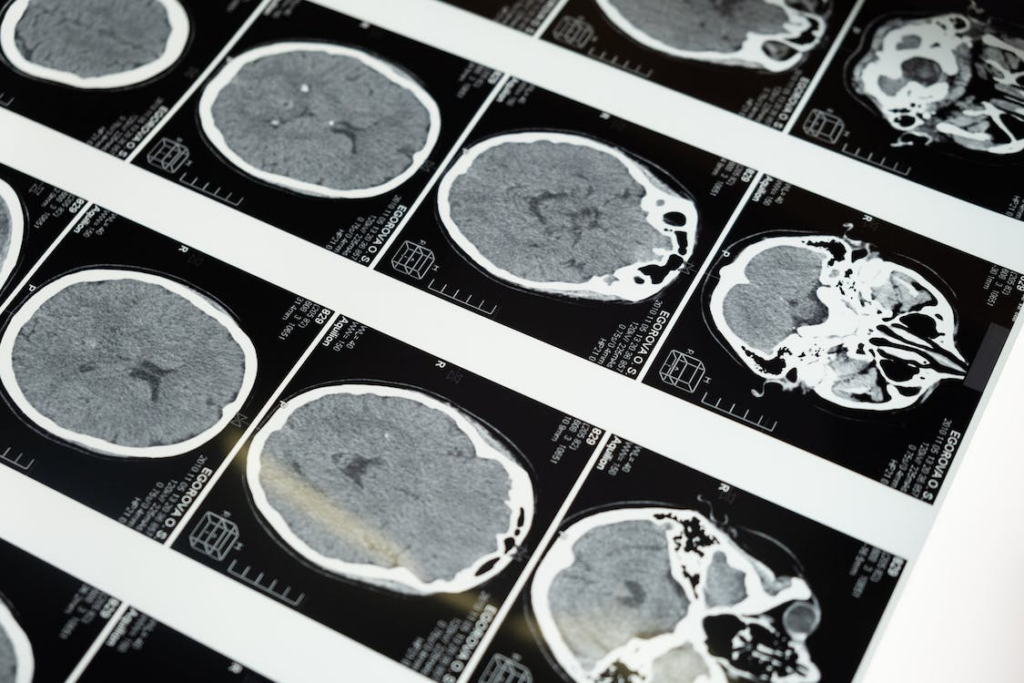
While battling the cancer, Lucas was unable to walk in a straight line and started losing consciousness and having random nosebleeds.
His prognosis were grim as per statistics only 10% of those diagnosed with this type of cancer survive more than two years, as per the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute.
That same statistics states that 98% of patients with the rare brain tumor will die within five years, and the prognosis are even worse for children who have a life expectation of just nine to 12 months following a diagnosis.
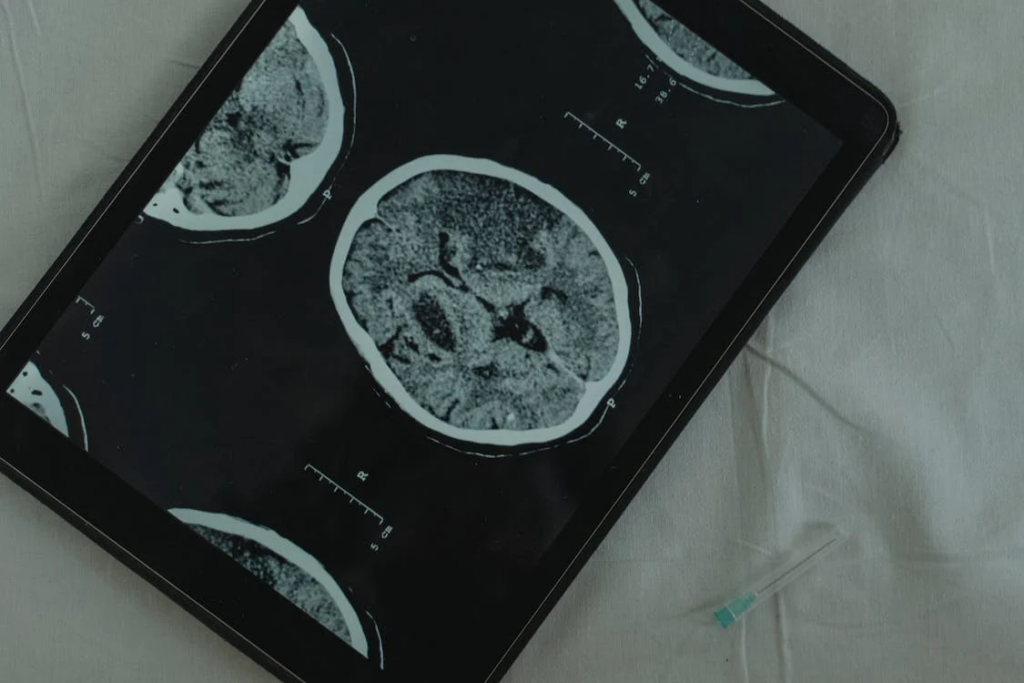
Today, at 13 years old, Lucas stands as a symbol of hope, having been in remission for an astounding five years.
Dr. Grill, head of the brain tumor program at the center, marvels at Lucas’s resilience, stating, “Lucas defied all odds. Over a series of MRI scans, I watched as the tumor completely disappeared.”
He added: “I don’t know of any other case like him in the world. Lucas’s tumour had an extremely rare mutation, which we believe made its cells far more sensitive to the drug.
“Lucas is believed to have had a particular form of the disease. We must understand what and why to succeed in medically reproducing in other patients what happened naturally with him.”
Researchers are now scrutinizing genetic anomalies and cultivating tumor organoids in laboratory settings, with Marie-Anne Debily, a researcher leading the laboratory efforts, highlighting the importance of identifying a drug capable of replicating the effects seen in Lucas’ tumor cells. “The next step will be to find a drug that has the same effect on tumor cells as these cellular changes,” she said.
However, “it takes 10-15 years from the first lead to become a drug – it’s a long and drawn-out process,” she added.
Please SHARE this article with your family and friends on Facebook.
Bored Daddy
Love and Peace
